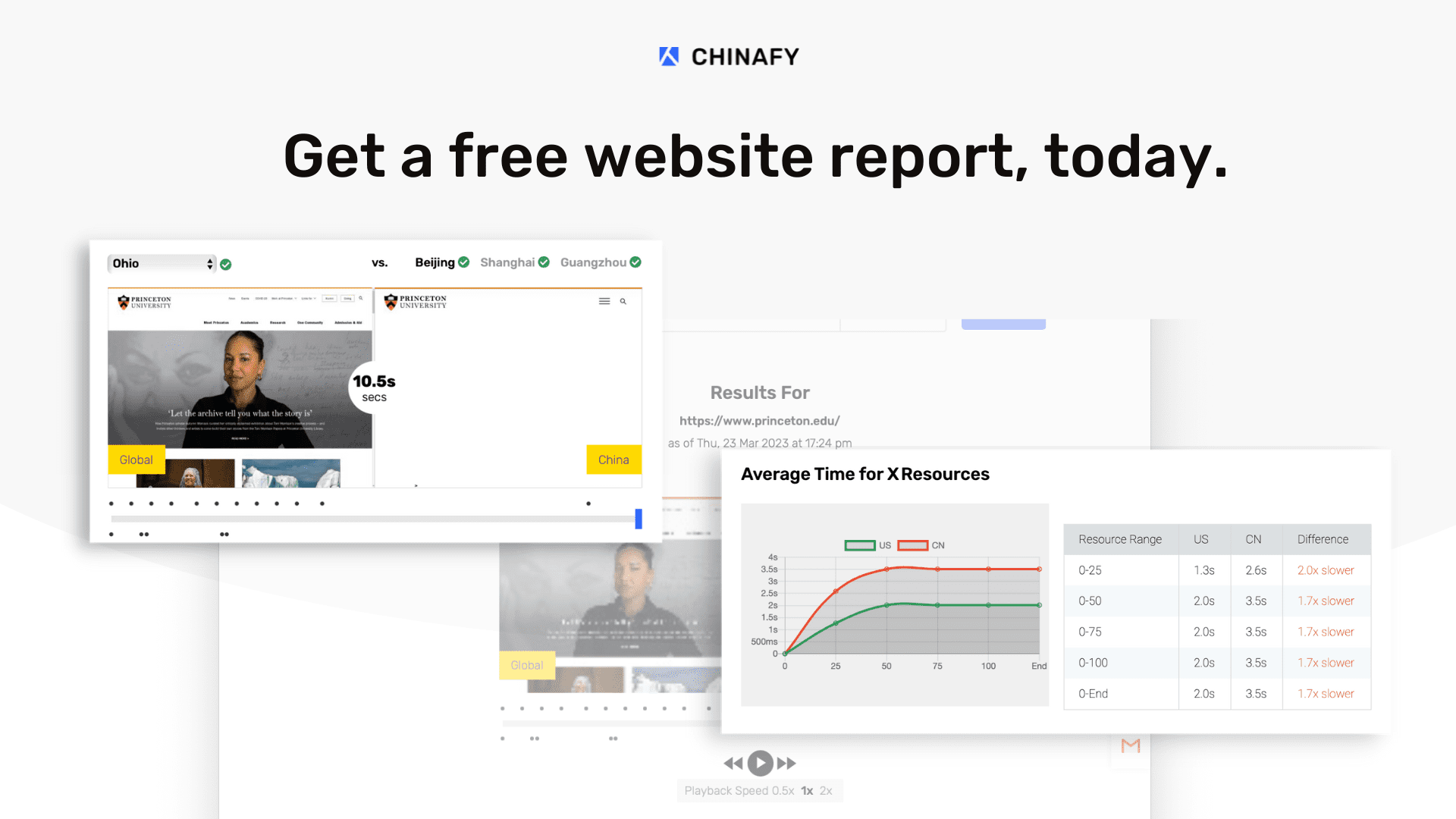
1 - Expected post-Chinafy results
The ultimate guide to Global Accelerators vs. CDNs: Key Differences and Use Cases for Content Delivery Networks in and outside of China
Table of contents:
What is a global accelerator
What is a content delivery network?
How do global accelerators differ from CDNs?
What are some key similarities & differences between global accelerators & CDNs?
Global accelerators & CDNs in the context of China
What is the difference between global accelerators, CDNs, and Chinafy?
Global accelerators & CDNs in the context of China
Not sure whether you need a global accelerator or CDN for your website?
Additional information on global accelerator providers & Chinafy partners
Speed and reliability of content delivery has become increasingly fundamental in ensuring a positive user experience for both websites and web applications.
Two of the most popular technologies for optimizing content delivery are global accelerators and content delivery networks (CDNs), each with their own unique strengths and limitations.
What is a global accelerator?
A global accelerator is a type of network service that is designed to speed up the delivery of internet content and applications to users across the globe. It works by routing traffic through a network of strategically located servers, known as points of presence (PoPs), that are optimized for delivering content to specific regions. Global accelerators typically use a variety of optimization techniques, such as caching, compression, and protocol optimization, to reduce latency and improve performance for end-users.
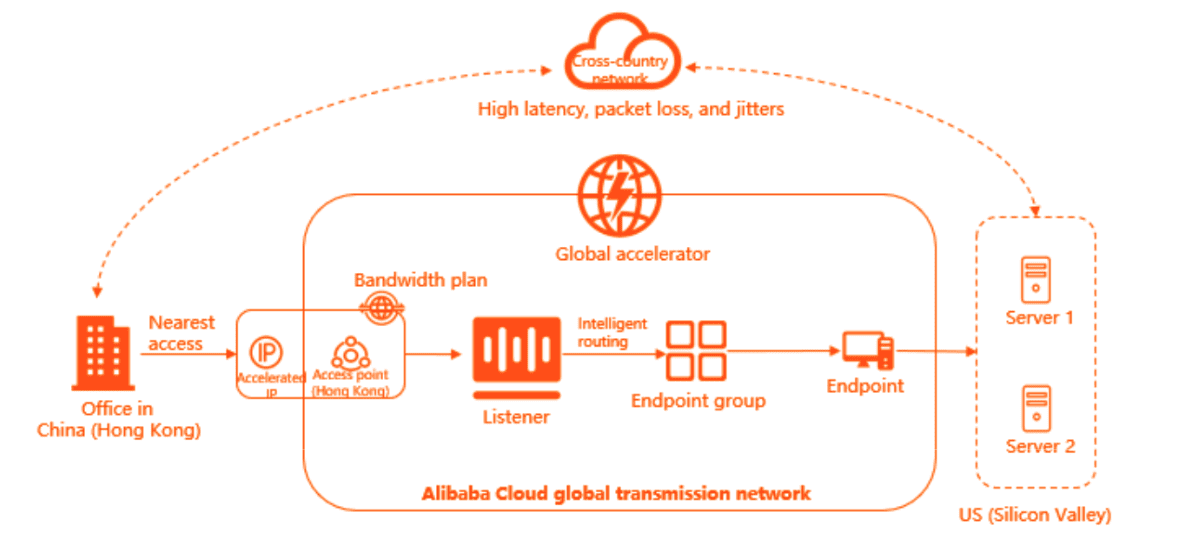
How Global Accelerator works (Source: Alibaba Cloud)
What is a content delivery network (CDN)?
On the other hand, a content delivery network (CDN) is also a network of servers that are used to deliver internet content and applications to end-users. However, a CDN typically stores and delivers static content, such as images, videos, and documents, from a network of edge servers that are distributed geographically closer to the end-users. This helps to reduce the distance that data needs to travel, which can result in faster delivery and reduced latency.
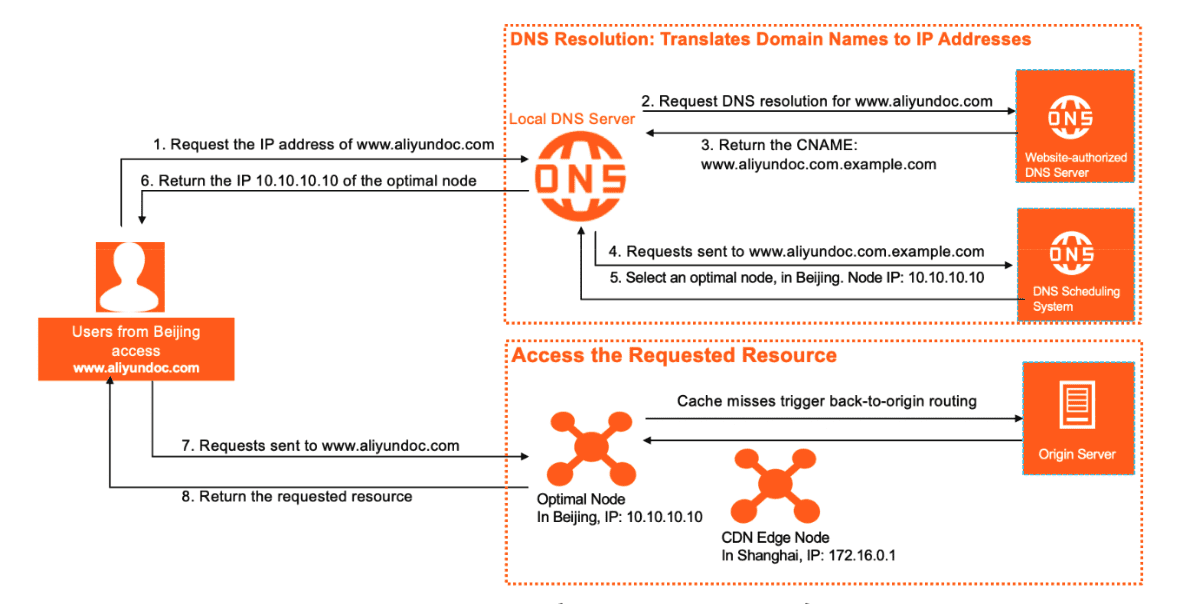
How CDN works (Source: Alibaba Cloud)
How do global accelerators differ from CDNs?
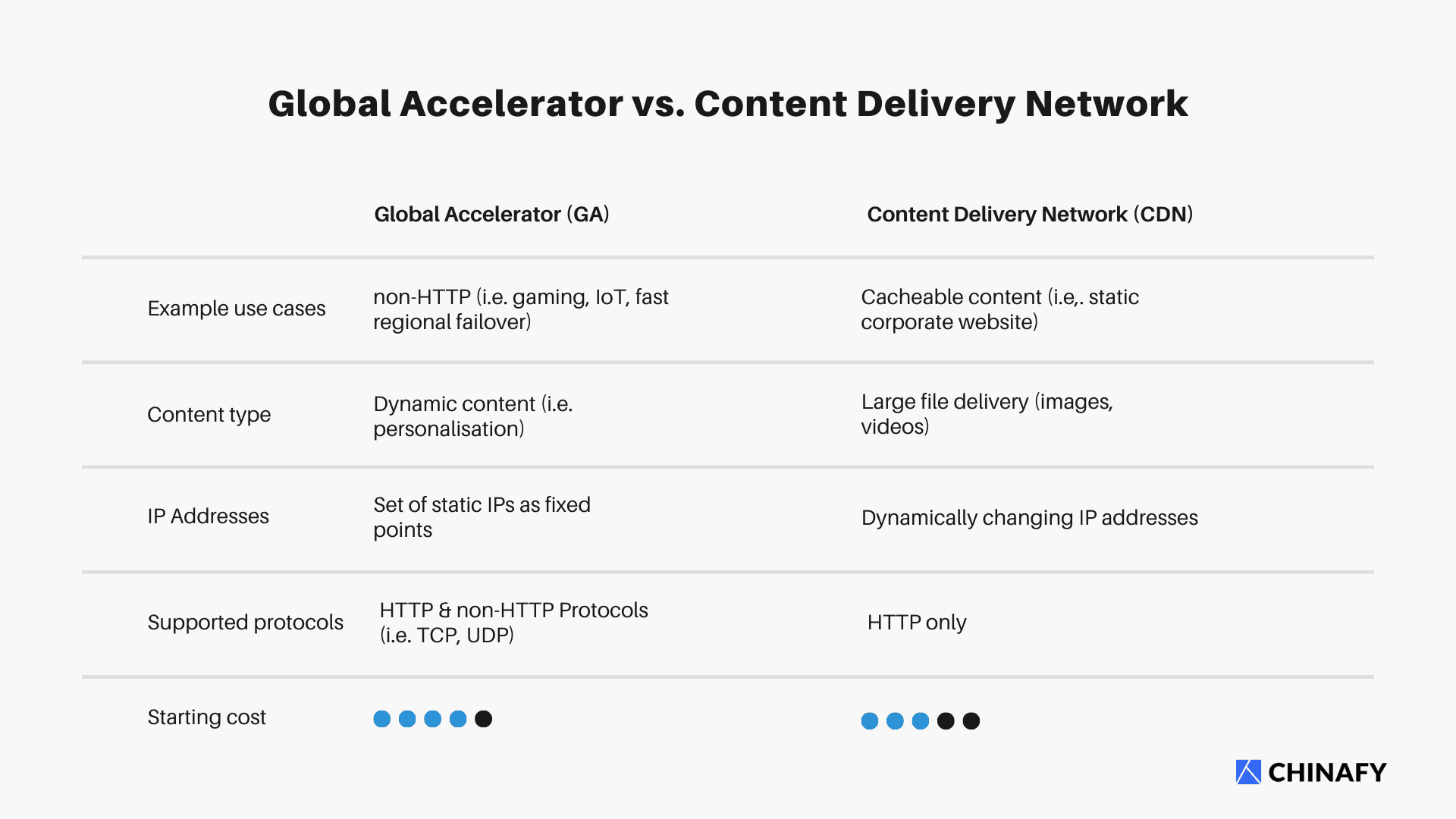
Both global accelerators and CDNs are designed to speed up content delivery and have similar limitations with respect to third party resources (more on this below), but they differ in terms of the types of content they optimize for and the techniques they use to do so.
Some typical use cases for either solutions are as follows:
Use cases for global accelerators:
Dynamic content and applications: Global accelerators are typically better suited for delivering dynamic content and applications, as they can optimize the delivery of data in real-time, and reduce the latency of interactive web applications.
Personalized content: If a website delivers personalized content to its users, a global accelerator can help to ensure that this content is delivered quickly and efficiently, even as it changes frequently.
API traffic: If a website relies on APIs to deliver data or services to its users, a global accelerator can help to ensure that API requests are fulfilled quickly and efficiently, even across long distances.
Use cases for CDNs:
Static content: CDNs are typically better suited for delivering static content, such as images, videos, and documents, as this content can be easily cached at edge servers and served to users quickly.
Large file delivery: If a website needs to deliver large files, such as software downloads or media files, a CDN can help to ensure that these files are delivered quickly and efficiently, even to users in remote regions.
Website performance: CDNs can also help to improve website performance by reducing the load on origin servers and improving the overall speed and responsiveness of the website.
While global accelerators are typically used for dynamic content and applications, CDNs are typically used for static content.
What are the similarities and differences between a Global Accelerator and a CDN?
Similarities between GA and CDN solutions
Both are designed to optimize content delivery and improve website and application performance for end-users.
Both use a network of servers located in strategic locations around the world to reduce latency and improve the speed of content delivery.
Both use caching to reduce the time it takes to deliver content to end-users.
Both can be used to improve website performance and reduce the load on origin servers.
Both global accelerators and CDNs are typically only applicable to resources on the primary domain, and may not be effective for delivering third-party resources such as ads or social media widgets. This is particularly important when it comes to China website delivery.
Learn more about how sites using global accelerators & CDN solutions work with Chinafy to improve performance & deliverability in China
Differences between GA and CDN solutions
Global accelerators are typically used for delivering dynamic content and applications, while CDNs are typically used for delivering static content, such as images, videos, and documents.
Global accelerators typically use a variety of optimization techniques, such as caching, compression, and protocol optimization, while CDNs may also use content optimization and traffic shaping to optimize content delivery.
Global accelerators may not be as effective for traffic that originates from regions that are far away from the nearest point of presence (PoP), while CDNs may not be effective for delivering fresh or frequently changing content.
Global accelerators tend to be more expensive than CDNs, particularly for businesses with high volumes of traffic or complex delivery requirements.
Global accelerators may be more expensive to implement and maintain than CDNs, particularly for small businesses or organizations with limited resources.
Global accelerators & CDNs in the context of China
When deciding whether you would require a global accelerator or CDN for China, it is first important to determine -
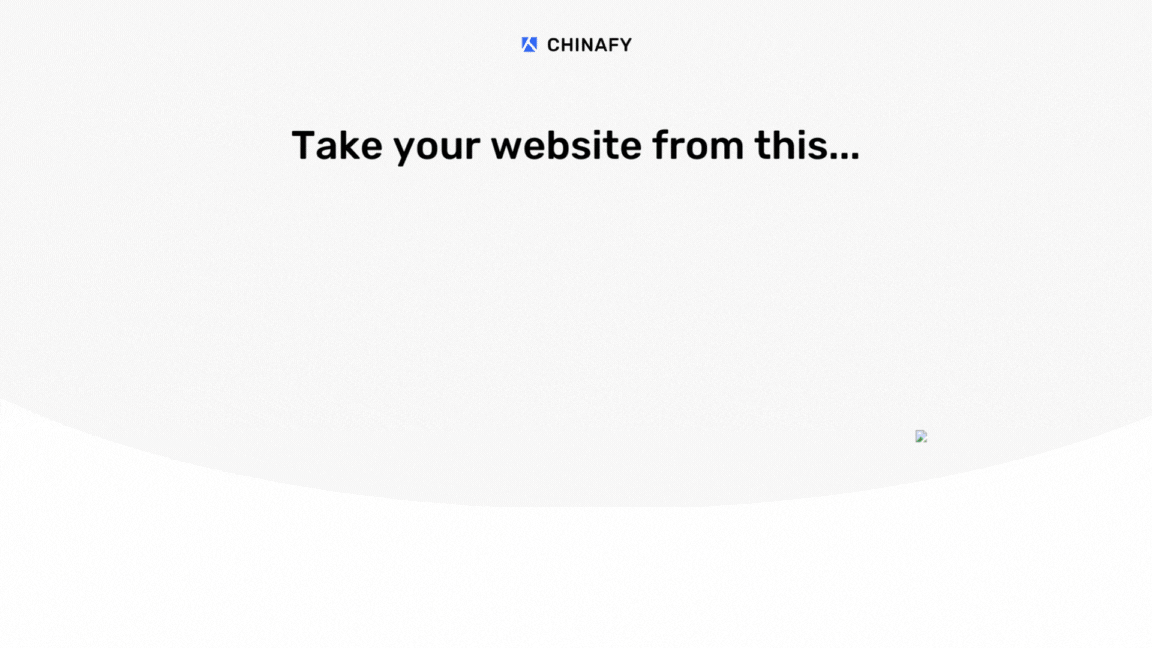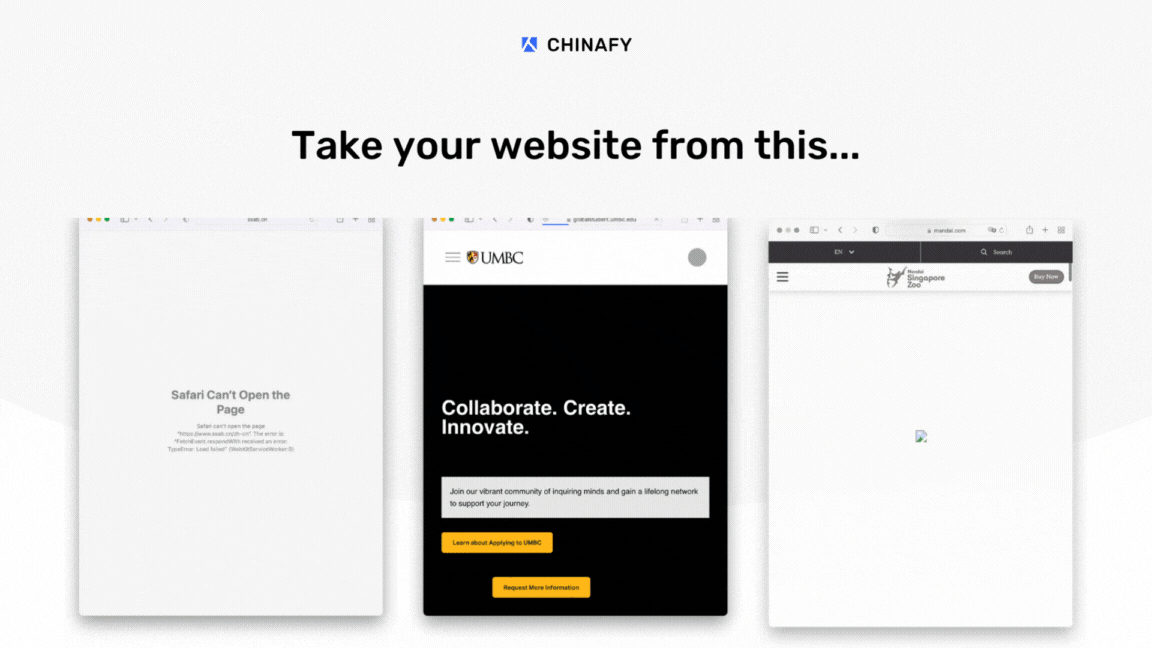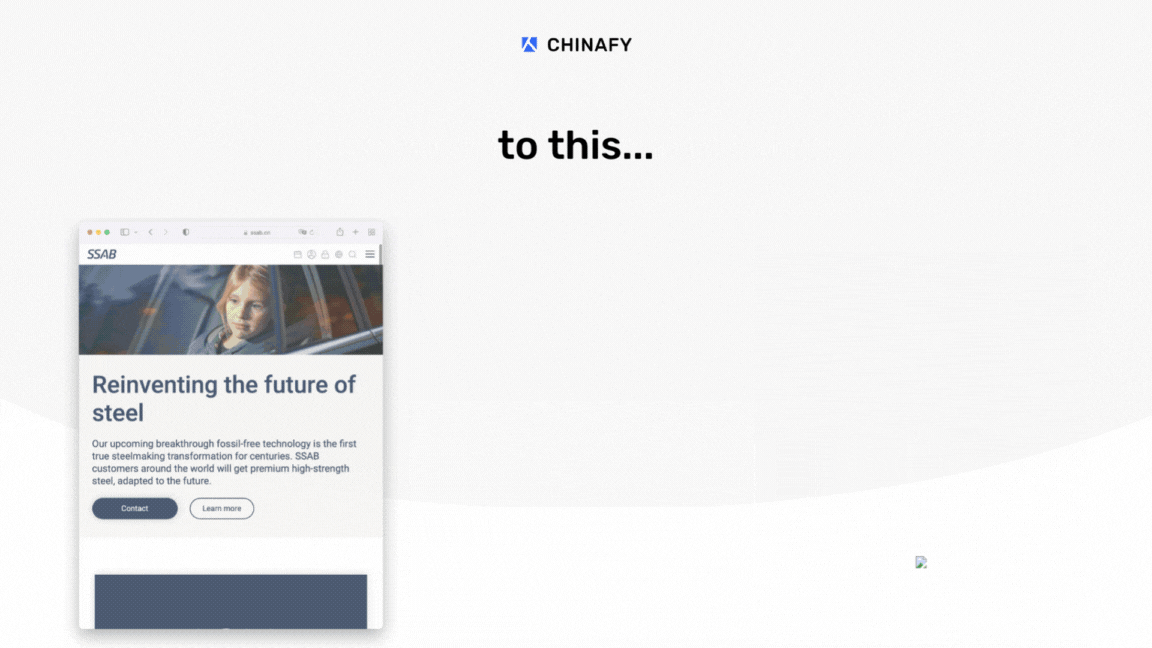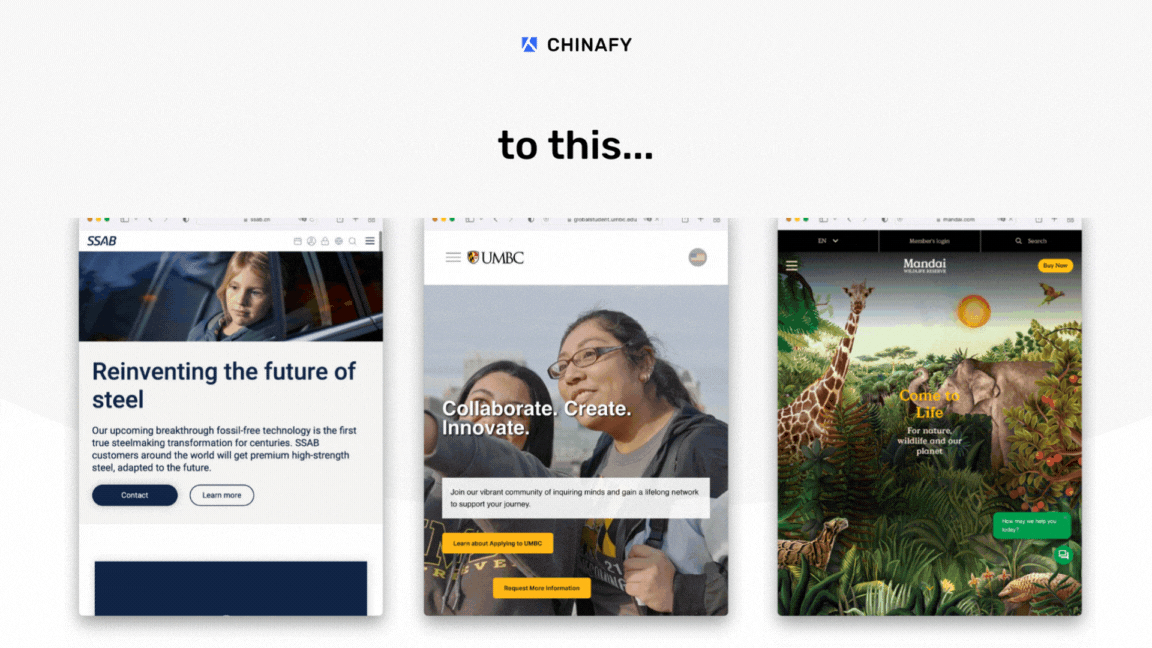
If your website is loading well or slowly in China?
Is it already using a global accelerator or CDN service?
Is it encountering performance issues beyond speed, like functionality or interactive components like videos, maps and forms?
It is understandable that companies are naturally inclined to immediately add a global accelerator, content delivery network, or additional hosting server when they discover their website is slow in China.
That is because, in most markets, taking these actions would help in overall performance. However, China is a unique case as a lot of performance issues stem from third-party resources and not primary resources (which are tackled by global accelerators and content delivery networks).
To best determine what components are needed for your technical stack, you must first identify what are the root causes behind performance of your website in China.
Why is my website slow in China?
What is the difference between global accelerators, CDNs, and Chinafy?
Neither global accelerators or content delivery networks are able to address inaccessible, or slow third party resources.
That’s why leading cloud providers that offer global accelerator solutions and CDNs partner with Chinafy, a China web compatibility platform that is uniquely able to scan, resolve and optimize these third party issues for a faster, fuller, secure delivery of a website in China.
Depending on your website and how it’s been built, global accelerator & content delivery solutions may be helpful in terms of overall improvement in primary resource delivery.
Global accelerator & CDN requirements in China
Overall, using any servers inside of China or services hosted in China requires careful compliance with regulatory and technical requirements, as well as a deep understanding of the local market and network conditions.
One such requirement is obtaining a ICP license.
Businesses that wish to operate a website or use a GA or CDN node in China must obtain an Internet Content Provider (ICP) license from the Chinese government. This license is required to host content within China and to use a CDN to deliver content to users within the country. A prerequisite to obtaining an ICP license is having a China business entity, among other things.
It is also important to note that non-China and China global accelerator and CDN solutions have different requirements, even if they are from the same provider. For example, AWS and AWS China are operationally different.
Not sure whether you need a global accelerator or CDN for your website?
In cases like this, deciding whether or not to host in China is a business decision versus a performance-based one, as the performance gains can be marginal.
It is for this reason that not all global, non-Chinese companies decide to pursue a business entity or ICP license in China if their primary goal is purely to have a performative web presence.
Get in touch with an expert at Chinafy via enterprise@chinafy.com or fill out the Get Started Form here
Additional information on global accelerator providers & Chinafy partners
Chinafy is partnered with a number of Tier 1 providers who offer complimentary services. Some examples of these partners who provide global accelerator services include the following companies.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Global Accelerator: AWS Global Accelerator is a fully managed network service that uses Amazon's global network to optimize the delivery of internet traffic to end-users. It offers automatic failover, health checks, and endpoint monitoring to ensure high availability and performance for applications running on AWS or on-premises.
Microsoft Azure Front Door: Azure Front Door is a global accelerator service that provides traffic management and load-balancing capabilities for internet-facing applications. It uses Microsoft's global network to optimize traffic delivery and offers features such as SSL offload, traffic routing, and health monitoring.
Google Cloud CDN Interconnect: Google Cloud CDN Interconnect is a network service that provides direct access to Google's edge points of presence (PoPs) for improved content delivery and reduced latency. It allows customers to connect their own infrastructure to Google's CDN using dedicated interconnects for improved performance.
Alibaba Cloud Global Acceleration Service: Alibaba Cloud Global Acceleration Service is a network service that provides global traffic acceleration for internet-facing applications. It offers optimized routing and caching to improve the delivery of dynamic content and supports acceleration for various protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, and UDP.



1 - Expected post-Chinafy results