1 - Expected post-Chinafy results
Differences between Baidu SEO and Google SEO
AI is reshaping search engines, but Google and Baidu are playing entirely different games. From censorship to language preferences and cutting-edge AI tools, let’s dive into the key differences in SEO for these two search giants.
Baidu and Google are fundamentally different in their approach to search engine optimization, driven by cultural, regulatory, and technical considerations. Below, we’ll dive into the key differences you should understand when optimizing your website for these two search giants.
TL;DR: Baidu SEO and Google SEO differ in their market focus, language requirements, content censorship, backlink strategies, and AI integration. Baidu prioritizes Simplified Chinese content, strict compliance with Chinese regulations, and local backlinks, while Google emphasizes multilingual support, content diversity, and advanced AI-driven personalization. Optimizing for Baidu requires a tailored approach to succeed in the Chinese market.
Market focus and language requirements
Google supports multiple languages and character sets as it is a global search engine. Its SEO strategies are designed to cater to an international audience, making language a less significant barrier compared to Baidu.
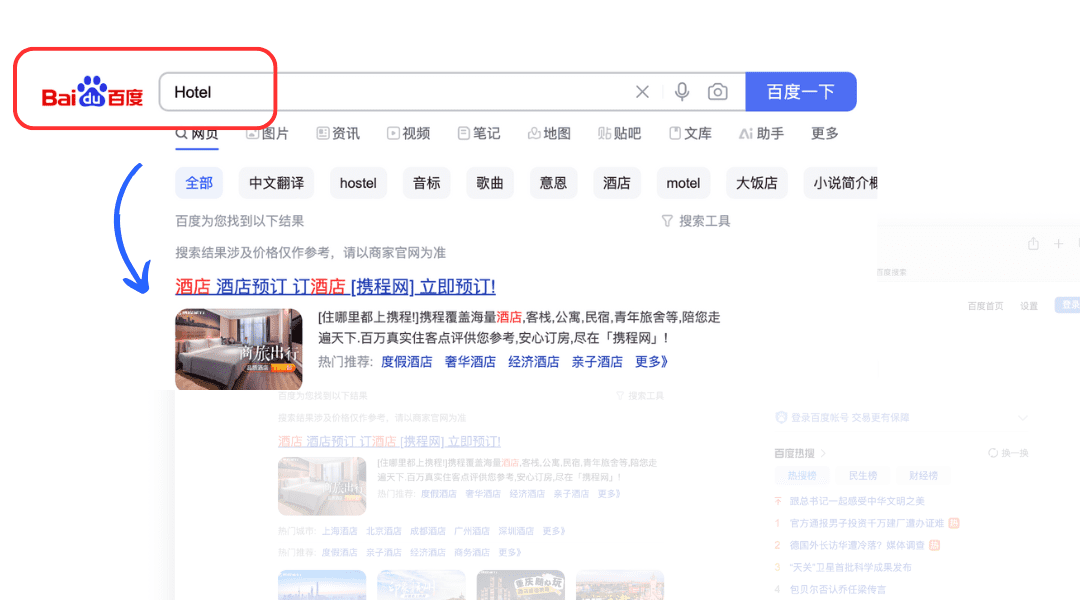
Baidu is laser-focused on the Chinese market. It prioritizes content in Simplified Chinese, and websites that lack localized Chinese content often see their rankings suffer. Even for non-Chinese queries, Baidu tends to favor Chinese-language content. Therefore, to effectively rank on Baidu, any content for the China market should be written in Simplified Chinese and cater to local cultural nuances.
Baidu 2024
Content compliance
Google generally operates with minimal content restrictions, allowing a wide range of topics to be explored. Content regulation primarily depends on local laws where Google operates.
Baidu operates under content regulations mandated by the Chinese government. Topics deemed politically sensitive or inappropriate may be regulated, which means that optimizing content for Baidu requires adhering to these guidelines. Content that falls afoul of these regulations can be penalized or entirely removed from search results.
Backlink strategy
Google uses a complex algorithm that evaluates the authority and relevance of backlinks from diverse domains globally. Quality, relevance, and diversity are the key metrics Google uses to evaluate backlinks.
Baidu places more weight on backlinks from Chinese websites, particularly those ending in .cn or .com.cn. Baidu's algorithm is less sophisticated in handling link spam, making it easier to manipulate rankings through low-quality links. However, this also means that recovery from penalties related to spammy backlinks can take a long time, so quality remains important.
Technical SEO and page load speed
Google focuses on a variety of technical SEO elements, including Core Web Vitals like LCP (Largest Contentful Paint), FID (First Input Delay), and CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift). Google emphasizes mobile-friendliness and overall user experience.
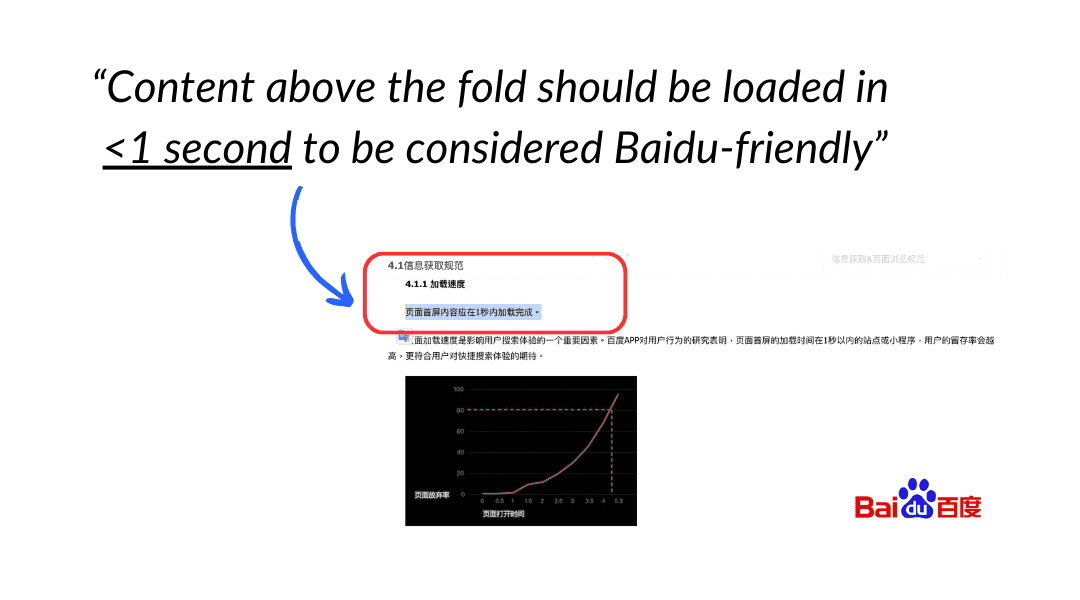
Baidu also values a fast user experience and tends to favor websites that load in under two seconds. Baidu’s crawlers struggle with JavaScript and AJAX, making it essential to use plain HTML wherever possible for better indexing. If your site has complex JavaScript elements, it might not perform as well on Baidu compared to Google. Most global sites suffer web performance issues in China because of infrastructure and code incompatibilities with China’s internet ecosystem. Resolving these issues goes beyond solely hosting your site in China or using a CDN. (Chinafy can improve your website’s speed and functionality in China without requiring a full onshore hosting solution.)
Baidu 2024
Local SEO and hosting considerations
Google local SEO is largely based on user location, and its ecosystem values tools like Google My Business to help boost visibility in local searches.
Baidu prioritizes local content and websites hosted in China with a .cn domain are more likely to rank higher. However, if your site is accessible from China and optimized for speed and functionality, it should still rank on Baidu even if it doesn’t use a Chinese domain. However, you may choose to go a step further and use a .cn domain.This however, does require a Chinese business entity and other pre-requisites.
Indexing speed and algorithm updates
Google has a sophisticated, dynamic indexing process and can often index new content in hours or even minutes. Google frequently updates its algorithm (about 500-600 times annually), which ensures the quality and relevance of its search results.
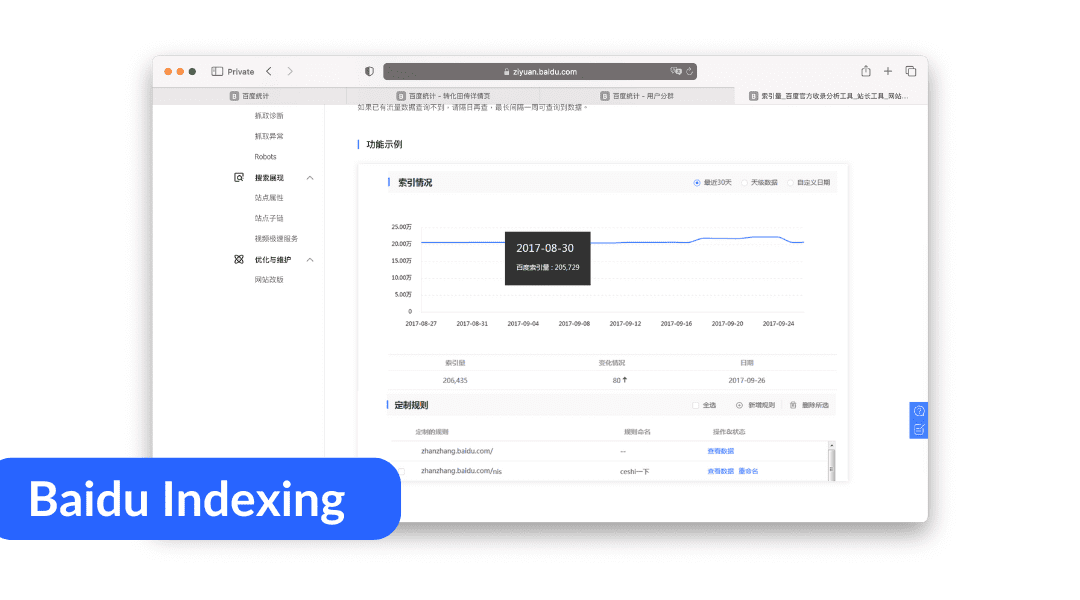
Baidu indexing is slower, often taking about a week for new content to appear in search results. Baidu's updates are less frequent and less transparent compared to Google's, focusing primarily on user preferences and local regulatory compliance rather than broader algorithmic innovations.
Baidu Indexing
User behavior and search preferences
Google users typically type out keywords or phrases, and Google's AI-driven features like autocomplete and natural language understanding make this seamless.
Baidu users often prefer selecting options from a list, rather than typing out entire search queries. This behavior stems from the complexity of typing in Chinese characters and has led Baidu to develop features like dropdown options to assist users in forming search queries.
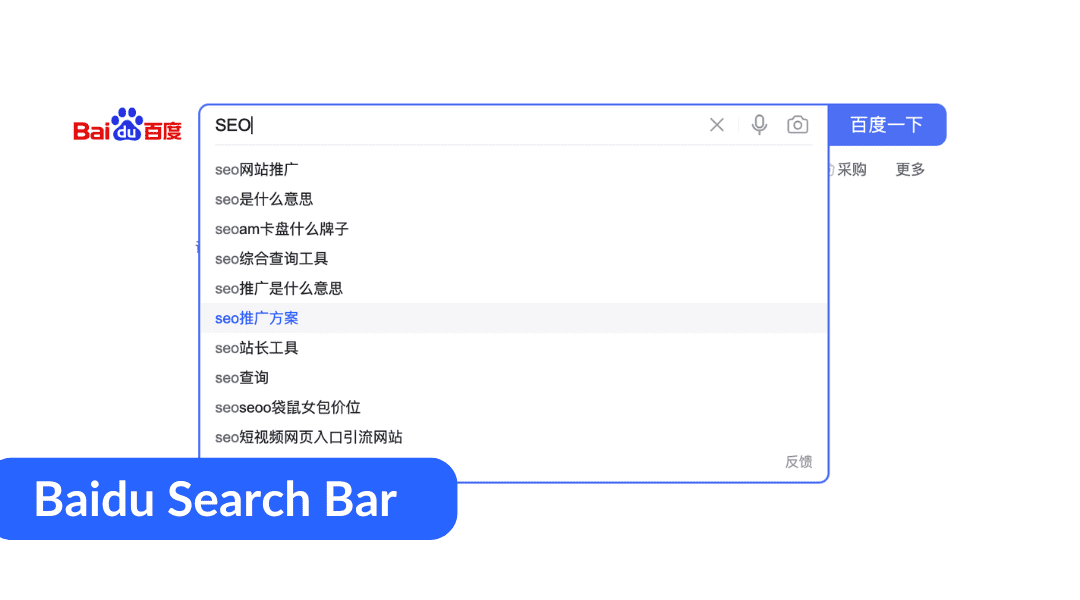
Baidu Search Bar
AI integration in search experience
Google uses AI models like RankBrain, BERT, and MUM to improve the understanding of user intent and context. These models help Google better comprehend complex and ambiguous queries, offering personalized results tailored to each user’s behavior and preferences. Google's use of featured snippets and knowledge panels also aims to improve user experience by providing direct answers to common queries.
Baidu has made significant investments in AI, particularly with the introduction of its ERNIE Bot, which enhances conversational search capabilities and provides more direct, contextually relevant answers. Features like Simple Search also enable dialogue-based interfaces and multimedia content to create a more enriched user experience.
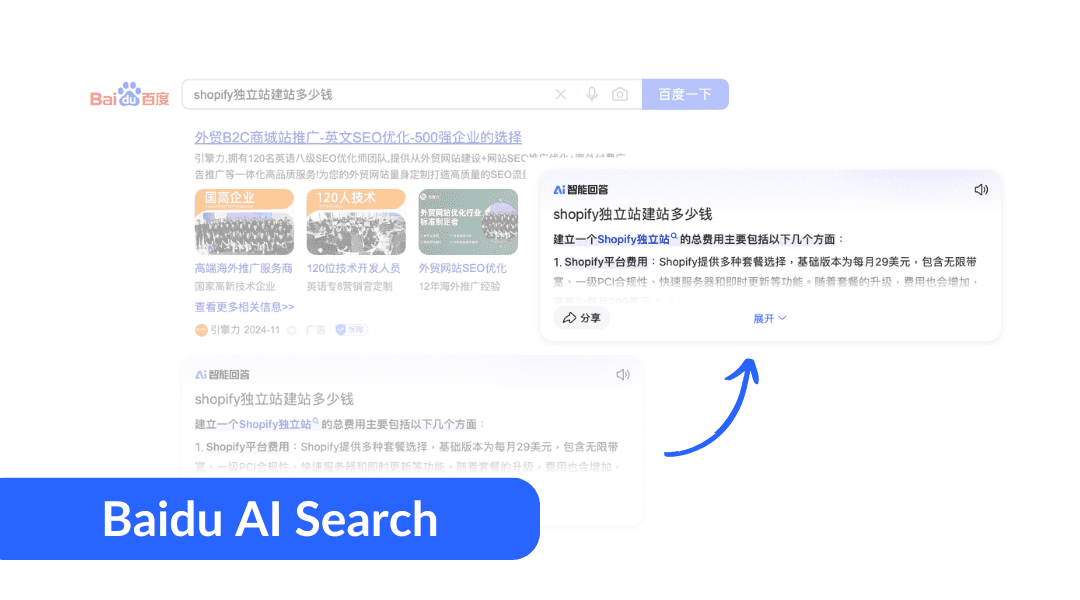
Baidu AI Search
While Google focuses on multilingual accessibility, content diversity, and advanced AI for personalization, Baidu is built around local relevance, regulatory compliance, and simplicity for Chinese users. Both search engines leverage AI, but each tailors its technologies to suit its primary audience.
Optimizing for Baidu requires a different mindset—one that prioritizes localization, Simplified Chinese content, fast-loading HTML pages, and strict compliance with Chinese content regulations. Chinafy can make your website run faster and fully in China as well as connect you with Baidu experts who can help you with your China marketing strategy beyond website optimization. Get started now.



1 - Expected post-Chinafy results